The 5 Lean Management Principles: Transform Your Business for Success
- Why Lean Management Matters
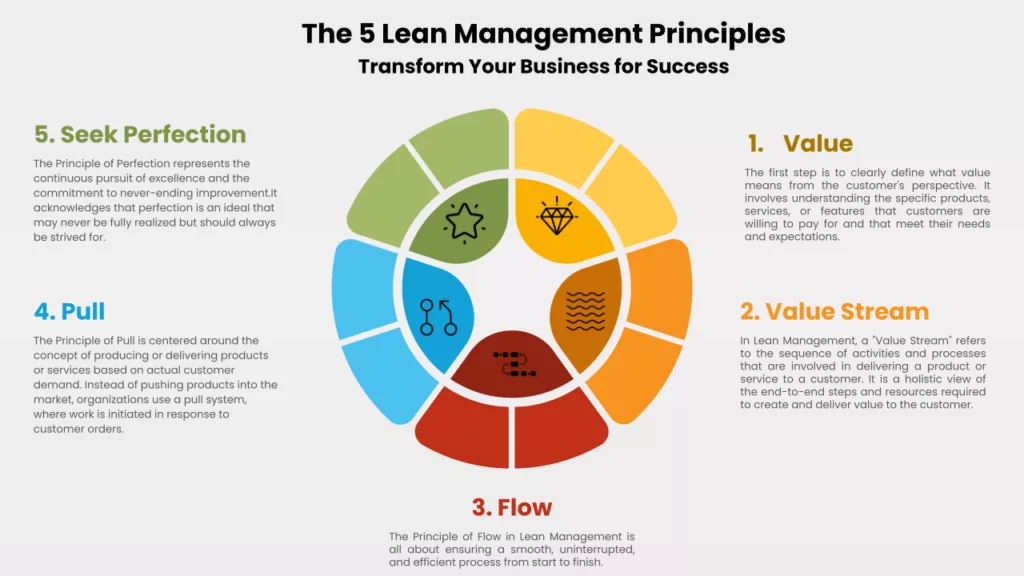
- 1. The Principle of Value
- 2. The Principle of Value Stream
- 3. The Principle of Flow
- 4. The Principle of Pull
- 5. The Principle of Perfection
- Lean Thinking: A Mindset for Success
- How to Implement Lean Principles in Your Organization?
- Conclusion: Transform Your Business with Lean Principles
- Key Takeaways
- FAQs
The 5 Lean Principles: Transform Your Business for Success
In today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and deliver greater value to their customers.
One methodology that has gained significant prominence in achieving these objectives is Lean Management. Lean Management principles have proven to be transformative, helping businesses streamline operations and optimize their processes.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the world of Lean Management and explore the five Lean principles that can revolutionize your business.
Why Lean Management Matters
Before we dive into the specifics of the five Lean principles, let’s take a moment to understand why Lean Management is worth your attention.
Lean Management is not just another management fad; it’s a proven approach that has helped countless organizations achieve remarkable success.
By implementing Lean principles, businesses can:
- Enhance Efficiency: Lean principles are designed to eliminate waste, improve processes, and optimize workflows. This results in higher productivity and efficiency across the organization.
- Deliver Customer Value: Lean Management places a strong emphasis on delivering value to the customer. By aligning operations with customer needs, organizations can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Reduce Costs: Lean principles identify and eliminate unnecessary expenses, making operations more cost-effective. This can lead to significant cost savings over time.
- Foster Continuous Improvement: Lean Management is not a one-time solution but a continuous journey of improvement. It encourages a culture of continuous learning and adaptation.
- Empower Employees: Lean principles respect and value the contributions of employees. Engaged and empowered employees are more likely to contribute their best efforts to the organization’s success.
Now that we understand the significance of Lean Management, let’s explore the five Lean principles that form the foundation of this transformative methodology.
1. The Principle of Value
What is the Principle of Value in Lean Management?
The Principle of Value in Lean Management is a foundational concept that centers around the idea of understanding and delivering value from the perspective of the customer. It is the first of the five Lean principles and serves as the starting point for implementing Lean practices in an organization.
Here’s a breakdown of the key elements of the Principle of Value:
- Defining Value: The first step is to clearly define what value means from the customer’s perspective. It involves understanding the specific products, services, or features that customers are willing to pay for and that meet their needs and expectations.
- Value Stream Mapping: To effectively provide value, organizations need to map out the entire value stream, which represents the end-to-end processes and activities involved in delivering a product or service. Value stream mapping helps identify areas where value is created and where waste may exist.
- Eliminating Waste: Once the value stream is mapped, the focus shifts to eliminating waste. Waste refers to any activity or process that does not directly contribute to delivering value to the customer. Lean principles emphasize the systematic identification and elimination of waste, which can include activities like overproduction, excess inventory, unnecessary transportation, and waiting times.
- Creating Value: After waste is eliminated, the organization’s efforts should be directed toward activities that create value for the customer. This means ensuring that every step in the workflow adds value in some way, whether by improving quality, reducing lead times, or meeting specific customer requirements.
- Customer-Centric Approach: The Principle of Value places a strong emphasis on aligning all aspects of the organization with the needs and expectations of the customer. This customer-centric approach ensures that the organization’s actions and processes are driven by the goal of delivering value to the end-user.
Overall, the Principle of Value is about shifting the organizational mindset from internal-focused processes to a customer-centric perspective. By understanding what customers truly value and aligning operations with those preferences, organizations can eliminate waste, improve efficiency, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Another example is that of a smartphone app. Let’s say you download a smartphone app. What do you care about as a user?
You want the app to work smoothly, do what it’s supposed to do, and not crash. In Lean terms:
- Defining Value: The value is in the app’s performance – it should work flawlessly and meet your needs.
- Value Stream: This could involve the development and testing process for the app. They want to make sure it’s bug-free and user-friendly.
- Eliminating Waste: Any coding errors, unnecessary features, or slow response times that don’t contribute to a great user experience would be considered waste.
In both examples, the Principle of Value is about focusing on what matters most to the customer and ensuring that everything in the process is aligned to deliver that value. It’s a way of thinking that helps organizations prioritize customer needs and eliminate anything that doesn’t contribute to those needs – just like making sure your pizza is hot and your app runs smoothly.
2. The Principle of Value Stream
In Lean Management, a “Value Stream” refers to the sequence of activities and processes that are involved in delivering a product or service to a customer. It is a holistic view of the end-to-end steps and resources required to create and deliver value to the customer.
A Value Stream typically includes:
- Value-Added Activities: These are the activities that directly contribute to meeting customer needs and expectations. They add value to the final product or service from the customer’s perspective. For example, in the context of pizza delivery, preparing the pizza, baking it, and delivering it to the customer’s door are all value-added activities because they directly contribute to providing the customer with a hot, delicious pizza.
- Non-Value-Added Activities (Waste): These are activities that do not add value from the customer’s perspective and are considered wasteful. In the pizza delivery example, any delays in taking the order, excessive waiting time, or unnecessary packaging can be seen as non-value-added activities because they don’t directly contribute to the customer’s satisfaction.
- Supporting Activities: These are necessary activities that may not directly add value but are required to support the value-added activities. For example, ordering supplies, maintaining equipment, and training employees are supporting activities in a pizza delivery operation. While they don’t directly make the pizza taste better, they are essential for the overall process.
By mapping the value stream, Lean practitioners can identify opportunities for improvement. They can streamline processes, eliminate waste, reduce delays, and optimize resource allocation to enhance efficiency and meet customer needs more effectively. Value Stream Mapping, a tool used in Lean Management, helps organizations visualize the current state of their processes and design a future state that is more efficient, customer-focused, and aligned with Lean principles. Ultimately, the goal is to create a value stream that delivers maximum value to the customer while minimizing waste and inefficiencies.
Let’s apply the Value Stream concept to the pizza delivery process, using your pizza order as an example:
- Step 1: Placing the Order
- Value Added Activity (From Customer’s Standpoint): You placing your order – this is what gets you closer to receiving your pizza.
- Non-Value Added Activity (Wasteful): Any unnecessary time spent on the phone, slow ordering process, or mistakes in taking your order would be wasteful.
- Step 2: Preparing the Pizza
- Value Added Activity (From Customer’s Standpoint): The chef making your pizza – this is what directly contributes to your satisfaction.
- Non-Value Added Activity (Wasteful): Delays in preparing your pizza, overcomplicated recipes that don’t improve taste, or excessive handling of ingredients are wasteful.
- Step 3: Baking the Pizza
- Value Added Activity (From Customer’s Standpoint): The time it spends in the oven, ensuring it’s cooked to perfection.
- Non-Value Added Activity (Wasteful): Overcooking or undercooking the pizza, excessive oven time, or letting it sit after baking without being delivered can be wasteful.
- Step 4: Packaging for Delivery
- Value Added Activity (From Customer’s Standpoint): The pizza being placed in a box, ready for delivery.
- Non-Value Added Activity (Wasteful): Complicated or time-consuming packaging, excessive use of packaging materials, or delays in this step are wasteful.
- Step 5: Delivery to Your Door
- Value Added Activity (From Customer’s Standpoint): The delivery driver bringing your pizza right to your doorstep.
- Non-Value Added Activity (Wasteful): Delays in delivery, getting lost along the way, or taking unnecessary detours would be wasteful.
In Value Stream Mapping, the goal is to identify and eliminate as many of these wasteful, non-value-added activities as possible. This leads to a more efficient process, faster delivery times, and a better experience for the customer. By focusing on what truly adds value and reducing everything else, Lean Management ensures you get your pizza as quickly and as deliciously as possible!
Examples of VALUE/VALUE STREAM MAPPING in different industries
Manufacturing: Lean in the Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, companies like Ford have employed Value Stream Mapping to optimize their production processes. They:
- Identify Bottlenecks: Use value stream maps to pinpoint areas where production bottlenecks occur, leading to delays.
- Optimize Workflow: Streamline the flow of work by eliminating unnecessary steps and redundancies in their assembly lines.
- Improve Communication: Enhance communication between different departments involved in the production process to minimize delays and errors.
Healthcare: Streamlining Patient Care
Hospitals utilize Value Stream Mapping to enhance the patient experience:
- Identify Bottlenecks: Identify areas in the patient journey where delays or inefficiencies occur, such as wait times for diagnostic tests.
- Optimize Workflow: Streamline the process of admitting patients, ensuring they receive timely care.
- Improve Communication: Enhance communication between healthcare providers and departments to minimize delays in patient care.
Software Development: Agile Sprint Planning
In the software development industry, Agile teams create sprint plans that act as value stream maps:
- Optimize Workflow: Adjust sprint plans to maximize efficiency by focusing on the most valuable features first.
- Identify Bottlenecks: Teams regularly review their sprint plans to identify any obstacles that may hinder project progress.
- Improve Communication: Regular stand-up meetings promote communication and collaboration among team members, reducing delays.
3. The Principle of Flow
The Principle of Flow in Lean Management is all about ensuring a smooth, uninterrupted, and efficient process from start to finish.
It’s like making sure everything flows seamlessly, just like a river, without any obstacles or delays.
It aims to eliminate interruptions, delays, and stoppages in the production or service delivery process.
Achieving a smooth flow of work is essential for reducing lead times, improving efficiency, and meeting customer demand effectively. To apply this principle, organizations must:
- Minimize Interruptions: Identify and eliminate anything that disrupts the flow of work. This may include unnecessary handoffs, waiting times, or process bottlenecks.
- Optimize Work Sequencing: Ensure that tasks are sequenced in a way that minimizes interruptions and maximizes efficiency. This may involve implementing a pull system.
- Respond to Changes Quickly: Develop the ability to adapt and respond quickly to changes in customer demand or market conditions.
- Waste Reduction: As interruptions and delays are reduced, waste is naturally minimized, leading to cost savings.
The Principle of Flow is about creating a workplace where work moves seamlessly, and processes are designed for efficiency. It contributes to better customer satisfaction, as products or services are delivered more predictably and on time.
Let’s apply the flow concept to the pizza delivery process:
- Step 1: Placing the Order
- In the context of Flow, this step should involve:
- Minimizing Interruptions: The customer places an order without any complications or interruptions, ensuring a smooth start to the process.
- Step 2: Preparing the Pizza
- For Flow, the pizza preparation should involve:
- Optimizing Work Sequencing: The chef works in a way that minimizes interruptions or delays in preparing the pizza, ensuring a continuous flow of work.
- Step 3: Baking the Pizza
- When it comes to Flow, baking the pizza should include:
- Minimizing Interruptions: The pizza goes into the oven without unnecessary delays, ensuring a continuous flow of the cooking process.
- Step 4: Packaging for Delivery
- In terms of Flow, packaging for delivery should involve:
- Optimizing Work Sequencing: The pizza is efficiently packaged, ensuring a smooth and fast transition to the next step.
- Step 5: Delivery to Your Door
- When focusing on Flow, the pizza delivery should include:
- Minimizing Interruptions: The delivery driver takes the shortest and most efficient route to your doorstep, minimizing delays and ensuring a smooth flow of the delivery process.
The Principle of Flow is like a well-orchestrated dance where every movement follows naturally, ensuring that your pizza is delivered hot and on time, just as you’d expect.
Manufacturing: Streamlining Production
In manufacturing, the Principle of Flow is evident in industries such as aerospace:
- Minimize Interruptions: Implementing Just-in-Time (JIT) production strategies to minimize interruptions and reduce the need for large inventories.
- Optimize Work Sequencing: Arranging tasks in a way that minimizes interruptions and ensures a smooth workflow.
- Respond to Changes Quickly: Adapting production schedules swiftly to accommodate changes in customer orders or design specifications.
Healthcare: Enhancing Patient Care Flow
In healthcare, the Principle of Flow is revolutionizing patient care:
- Minimize Interruptions: Hospitals minimize disruptions in patient care by optimizing nurse rounds and medication administration schedules.
- Optimize Work Sequencing: Ensuring that tests, consultations, and treatments are scheduled efficiently to minimize patient waiting times.
- Respond to Changes Quickly: Adjusting staffing levels and resources in response to fluctuations in patient volumes.
Software Development: Continuous Integration and Deployment
In software development, the Principle of Flow is integral to Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD):
- Minimize Interruptions: Automated CI/CD pipelines reduce manual intervention, ensuring a smooth flow from development to production.
- Optimize Work Sequencing: Prioritizing smaller, valuable code changes ensures a streamlined deployment process.
- Respond to Changes Quickly: Automatic rollback mechanisms enable rapid responses to unexpected issues during deployment.
4. The Principle of Pull
The Principle of Pull is centered around the concept of producing or delivering products or services based on actual customer demand.
Instead of pushing products into the market, organizations use a pull system, where work is initiated in response to customer orders.
Think of it as ordering exactly what you want, when you want it, rather than getting something that’s been sitting around.
In a pull system:
- Work is only started when there is a customer order or demand, ensuring that resources are not wasted on producing items that may not be needed.
- Inventory levels are reduced, as goods are produced in response to specific orders rather than being stockpiled.
- Customer preferences are better accommodated, as products are tailored to meet their exact requirements.
- Overproduction and excess inventory, which are forms of waste, are significantly reduced.
The Principle of Pull is an essential component of Lean Management, as it helps organizations operate with minimal waste and efficiently meet customer needs. Implementing a pull system often requires changes to production and supply chain processes, but the benefits are substantial.
Let’s apply this concept to the pizza delivery process:
- Step 1: Placing the Order
- Pull Principle: You place an order when you want a pizza. The pizza place doesn’t start making it until you request it. This is like “pulling” the pizza into production based on your demand.
- Step 2: Preparing the Pizza
- Pull Principle: Once you’ve placed your order, the kitchen starts making your pizza. They don’t start preparing it in advance; they respond to your request.
- Step 3: Baking the Pizza
- Pull Principle: The pizza goes into the oven as soon as it’s prepared, based on your order. There’s no pre-made pizza waiting to be baked; it’s all based on demand.
- Step 4: Packaging for Delivery
- Pull Principle: The pizza is packaged for delivery only when it’s ready to go. There’s no pre-packaging; it’s done in response to your order.
- Step 5: Delivery to Your Door
- Pull Principle: The delivery driver sets out to deliver your pizza as soon as it’s ready. They don’t wait around; they respond to the demand created by your order.
In essence, the Pull Principle ensures that every step in the pizza delivery process is initiated in direct response to your order. It minimizes waste, such as pizzas sitting around getting cold, and ensures that you receive a freshly made pizza, exactly when you want it. It’s like customizing your experience, getting a pizza made just for you, as if the whole process revolves around your preferences and timing.
Manufacturing: Pull Systems in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, the Principle of Pull is exemplified by companies like Dell:
- Work Based on Demand: Dell builds computers based on customer orders, reducing excess inventory.
- Minimize Inventory: Dell’s lean approach minimizes the need for large warehouses of pre-built systems.
- Customization: Offering customization options allows customers to pull products tailored to their specific needs.
Healthcare: Patient-Centered Care
In healthcare, patient-centered care aligns with the Principle of Pull:
- Work Based on Demand: Hospitals provide treatments and tests based on the specific needs and conditions of patients.
- Minimize Inventory: Avoiding overstock of medications and medical supplies reduces waste.
- Customization: Tailoring treatment plans and medications to individual patient needs.
Software Development: Agile Pull Systems
In software development, Agile methodologies embody the Principle of Pull:
- Work Based on Demand: Agile teams work on tasks based on customer or stakeholder priorities, ensuring that valuable features are developed first.
- Minimize Inventory: Agile teams avoid accumulating a backlog of unfinished work, reducing unnecessary work in progress.
- Customization: Adapting development efforts to meet changing customer requirements and feedback.
5. The Principle of Perfection
The Principle of Perfection represents the continuous pursuit of excellence and the commitment to never-ending improvement.
It acknowledges that perfection is an ideal that may never be fully realized but should always be strived for.
To embrace the Principle of Perfection, organizations must:
- Cultivate a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Encourage employees at all levels to seek out opportunities for improvement and make incremental changes.
- Set Ambitious Goals: Establish challenging but achievable goals for efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction.
- Measure Progress: Continuously monitor and measure key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress toward perfection.
- Empower Employees: Provide the training and tools necessary for employees to contribute to the ongoing improvement process.
The Principle of Perfection is not about achieving a static state of perfection but rather a commitment to constantly improving processes, products, and services. By embracing this principle, organizations can remain competitive and agile in an ever-changing business environment.
Let’s explore how this principle applies to the pizza delivery process:
- Step 1: Placing the Order
- Pursuit of Perfection: The pizza place aims to make the ordering process as seamless and efficient as possible. They strive to take your order accurately, quickly, and with the utmost courtesy. This ensures a perfect start to your pizza experience.
- Step 2: Preparing the Pizza
- Pursuit of Perfection: In the kitchen, the chef focuses on creating a pizza that meets the highest standards of taste, using the freshest ingredients and expert techniques. This pursuit of perfection ensures that your pizza is as delicious as it can be.
- Step 3: Baking the Pizza
- Pursuit of Perfection: The pizza is baked to perfection, with precise timing and temperature control to achieve the ideal crust, cheese melt, and toppings. This commitment to excellence ensures that your pizza is cooked just right.
- Step 4: Packaging for Delivery
- Pursuit of Perfection: The packaging process is designed to keep your pizza hot and fresh during delivery, with attention to detail to prevent any spillage or damage. This ensures that your pizza arrives in perfect condition.
- Step 5: Delivery to Your Door
- Pursuit of Perfection: The delivery driver is trained to provide a seamless and courteous delivery experience. They strive to arrive promptly, handle your pizza with care, and ensure your satisfaction.
In each step of the pizza delivery process, the Principle of Perfection is evident in the commitment to achieving the best possible outcome. It’s about continuous improvement and attention to detail, with the goal of delivering a perfect pizza and a perfect customer experience every time. The pursuit of perfection in Lean Management ensures that the pizza you receive is not just good but consistently outstanding.
Manufacturing: Continuous Improvement in Production
In manufacturing, the Principle of Perfection drives companies like Boeing:
- Cultivate a Culture of Improvement: Boeing encourages employees at all levels to suggest and implement improvements in production processes.
- Set Ambitious Goals: The company continually sets goals to improve production efficiency and reduce defects.
- Measure Progress: Boeing tracks key performance indicators (KPIs) to gauge progress and identify areas for further improvement.
Healthcare: Quality Improvement Initiatives
In healthcare, quality improvement initiatives align with the Principle of Perfection:
Cultivate a Culture of Improvement**: Hospitals and healthcare providers promote a culture where staff actively seeks opportunities for enhancing patient care, reducing medical errors, and improving outcomes.
- Set Ambitious Goals: Healthcare institutions set ambitious quality and safety goals, such as reducing hospital-acquired infections or improving patient satisfaction scores.
- Measure Progress: Hospitals track and analyze data on patient outcomes, readmission rates, and process performance to measure progress and make data-driven improvements.
Software Development: Agile Retrospectives
In software development, Agile retrospectives are a prime example of the Principle of Perfection:
- Cultivate a Culture of Improvement: Agile teams hold regular retrospectives to reflect on their performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Set Ambitious Goals: Teams set sprint goals and continuously aim for improved velocity, quality, and customer satisfaction.
- Measure Progress: Agile teams use metrics such as velocity, burndown charts, and defect counts to assess their progress and adapt their processes accordingly.
Lean Thinking: A Mindset for Success
Lean thinking is not just a set of tools or principles; it’s a mindset that permeates an organization. It’s about viewing every aspect of the business through the lens of Lean principles and striving for continuous improvement.
Lean thinking encourages organizations to:
- Challenge the Status Quo: Continually question existing processes and practices to identify areas for improvement.
- Empower Employees: Give employees the autonomy and authority to make decisions that contribute to Lean objectives.
- Value-Centric Approach: Place a strong emphasis on delivering value to the customer and aligning all activities with customer needs.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Rely on data and metrics to drive decision-making and measure progress.
By embracing Lean thinking as a core mindset, organizations can create a culture of innovation and continuous improvement that sets the stage for long-term success.
How to Implement Lean Principles in Your Organization?
Implementing Lean principles can be a transformative journey for any organization, but it requires commitment, dedication, and a structured approach.
Here are the key steps to implementing Lean principles in your organization
- Leadership Commitment: Ensure that top leadership is committed to Lean principles and actively supports the implementation process.
- Education and Training: Provide employees with the necessary training and education to understand Lean concepts and principles.
- Identify Value: Work with cross-functional teams to identify and understand the value that the organization delivers to its customers.
- Map Processes: Map the value stream to gain insights into current processes and identify areas for improvement.
- Eliminate Waste: Systematically eliminate waste by addressing bottlenecks, improving flow, and optimizing processes.
- Implement Lean Tools: Utilize Lean tools and techniques, such as 5S, Kanban, and Kaizen, to drive improvements.
- Measure Progress: Continuously monitor and measure key performance indicators to track progress and make data-driven decisions.
- Empower Employees: Encourage and empower employees at all levels to participate in the Lean transformation and suggest improvements.
- Sustain the Change: Ensure that Lean principles become part of the organization’s DNA and that the culture of continuous improvement is maintained.
- Celebrate Success: Recognize and celebrate achievements and improvements resulting from Lean implementation.
Conclusion: Transform Your Business with Lean Principles
In today’s competitive business landscape, the adoption of Lean principles is not just a choice; it’s a necessity for organizations aiming to thrive and excel. The five Lean principles—Value, Value Stream Mapping, Flow, Pull, and Perfection—provide a roadmap for businesses to optimize processes, reduce waste, and deliver greater value to their customers.
By applying Lean principles to various aspects of your organization, from manufacturing to project management, and by fostering a Lean thinking mindset, you can embark on a journey of continuous improvement that will lead to higher efficiency, lower costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Remember, Lean principles are not a one-time solution but a path to sustained success. Embrace Lean Management, implement its principles, and watch your organization transform into a lean, efficient, and customer-focused powerhouse.
Key Takeaways
- Lean principles are a proven approach to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and deliver value to customers.
- The five Lean principles are Value, Value Stream Mapping, Flow, Pull, and Perfection.
- Lean principles can be applied to project management, manufacturing, and other areas of business.
- Lean thinking is a mindset that promotes continuous improvement and customer-centricity.
- Implementing Lean requires commitment, training, and a structured approach.
FAQs
What are the 5 lean management principles?
A: The 5 lean management principles are value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection.
How can lean management benefit my organization?
A: Lean management can benefit your organization by reducing waste, improving efficiency, increasing productivity, enhancing quality, and empowering employees.
What is lean manufacturing?
A: Lean manufacturing is a systematic approach to eliminating waste and maximizing value in the production process.
How does lean management relate to project management?
A: Lean management principles can be applied to project management to improve project outcomes by minimizing waste, optimizing resources, and increasing project flow.
What are the key principles of lean management?
A: The key principles of lean management are identifying value, mapping the value stream, creating flow, establishing pull, and pursuing perfection.
How did lean management emerge?
A: Lean management emerged from the Toyota Production System, a management philosophy developed by Toyota to improve efficiency and eliminate waste.
What is the role of lean management in process improvement?
A: Lean management provides a structured approach to process improvement by systematically identifying and eliminating waste, and continuously improving processes.
What is the concept of “flow” in lean management?
A: The concept of “flow” in lean management refers to the smooth and uninterrupted movement of work through the value stream, without delays or bottlenecks.
How can lean management benefit customer satisfaction?
A: Lean management focuses on meeting the needs of the customer by delivering value and eliminating waste, resulting in improved customer satisfaction.
What is the role of the “respect for people” principle in lean management?
A: The “respect for people” principle in lean management emphasizes the importance of treating employees with dignity and involving them in decision-making processes, leading to a more engaged and motivated workforce.




